Environment variables with Python
When we need to use secret data on our apps (such as API keys or whatever), we can set environment variables and then:
- using the
oslibrary (for most Python apps and Jupyter notebooks) - using the
google.colab.userdatalibrary (for Google Colab notebooks)
Python apps and Jupyter notebooks
Setting the "secret" variables
We can set the secret variable up in two ways:
Operating system wide
On a Mac or on a Linux, running this command on the Terminal from any folder will set the variable for use across the entire system:
export SECRET_NAME="secret_value_here"On Windows, just go to Command Prompt:
C:\> set SECRET_NAME=secret_valueThis way works if we know that we will use this variable across almost every app but we should try the next way for project-specific secret variables!
On an .env file
For project-specific secrets, create a file named .env and fill it with as many variables as needed, e.g.:
SECRET_NAME_1="secret_value_1_here"
SECRET_NAME_2="secret_value_2_here"Let's also not forget to include .env in the .gitignore file to keep the secrets, secret!
Using them in a Python file
Now, we can use them in our Python program (but not without the os library):
# apiapp.py
import os
# if using .env file
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
secret = os.environ.get("SECRET_NAME")
# another example
api_key = os.environ.get("MY_SECRET_API_KEY")
# rest of program - happy coding!Google Colab notebooks
In a Google Colab notebook, things happen more easily:
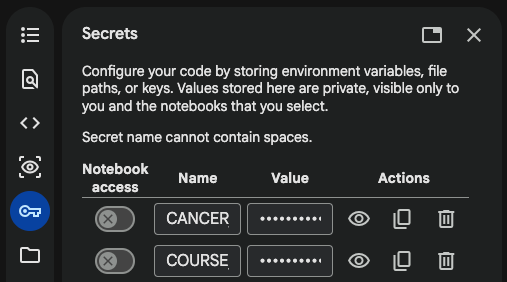
- click on the "key" icon on the left-side navigation menu
- click on "+ Add new secret"
- turn the "Notebook access" switch to the "on" position
- enter the secret name under "Name"
- enter the secret value under "Value"
Then, in the code:
from google.colab import userdata
my_secret = userdata.get('SECRET_NAME')Google Colab will show us something like:
from google.colab import userdata
userdata.get('SECRET_NAME')...but should show us that we can actually use it in a variable ;)